Lab 1 Git operations and Github
Lab 1 Git operations and Github
Revisit Git operations
init a git repository
cd new_project_folder
git init
Managing repository remote sites
git remote -v
git remote add
git remote add name URL
git remote remove
git remote remove name
git remote rename
git remote rename name new_name
Managing files in stage for commit
git add
git add pattern
Here are some common patterns
.mean all files*.jsmeans all js filesfolderall files under the folderfolder/*.jsall js files under the folder
git status
You could view the staged files with git status.
git status
reset
git reset
commit and push
commit
git commit
Options
- -m “message”
- -a
push
git push -u origin master
Download changes from remote
fetch
pull
More Git operations
Fork
Fork means cloning a repository from other and continue to work on it by yourself. It may or may not merge back to original depending on your need.
To fork a repository on Github, simply click on the top right Fork button. You will given a list for selecting destination of your fork.
After that, you would have your own copy of the repository.
Basic Branching
A branch in Git is simply a lightweight movable pointer to one of these commits. The default branch name in Git is master . As you start makingcommits, you’re given a master branch that points to the last commit you made. Every time you commit, it moves forward automatically.
After cloning the repository to local computer, you could create a new branch for development. To create a new branch, we use git checkout command. Here is an example usage of this command. It would create a new branch with name iss53 in your local repository.
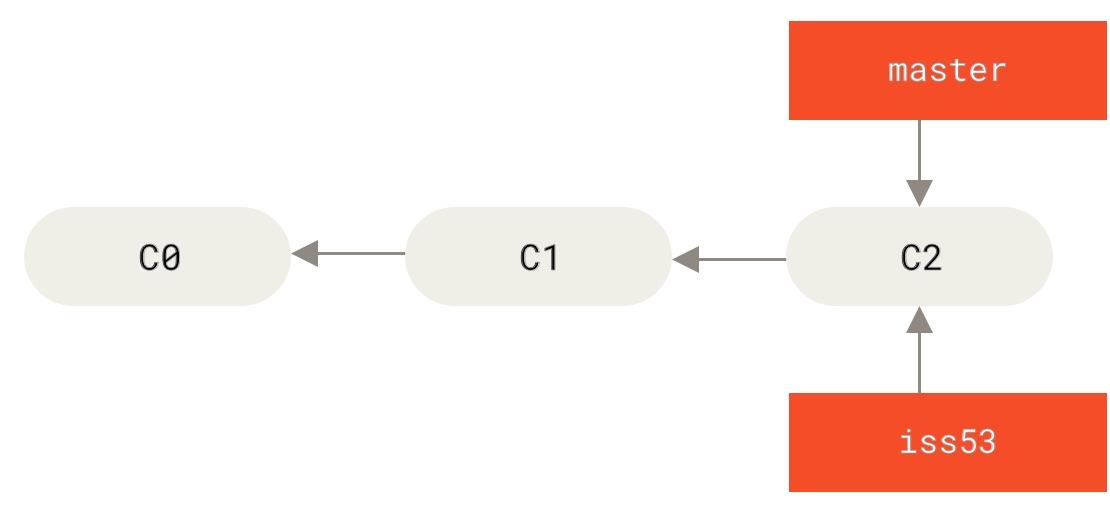
git checkout -b iss53
After you did some changes and committed, you could push your local branch to remote by the following command.
git push -u origin iss53
Basic Merging
After you have completed a single feature of your system, the repository maintainer would merge your commit to the master branch for deployment.
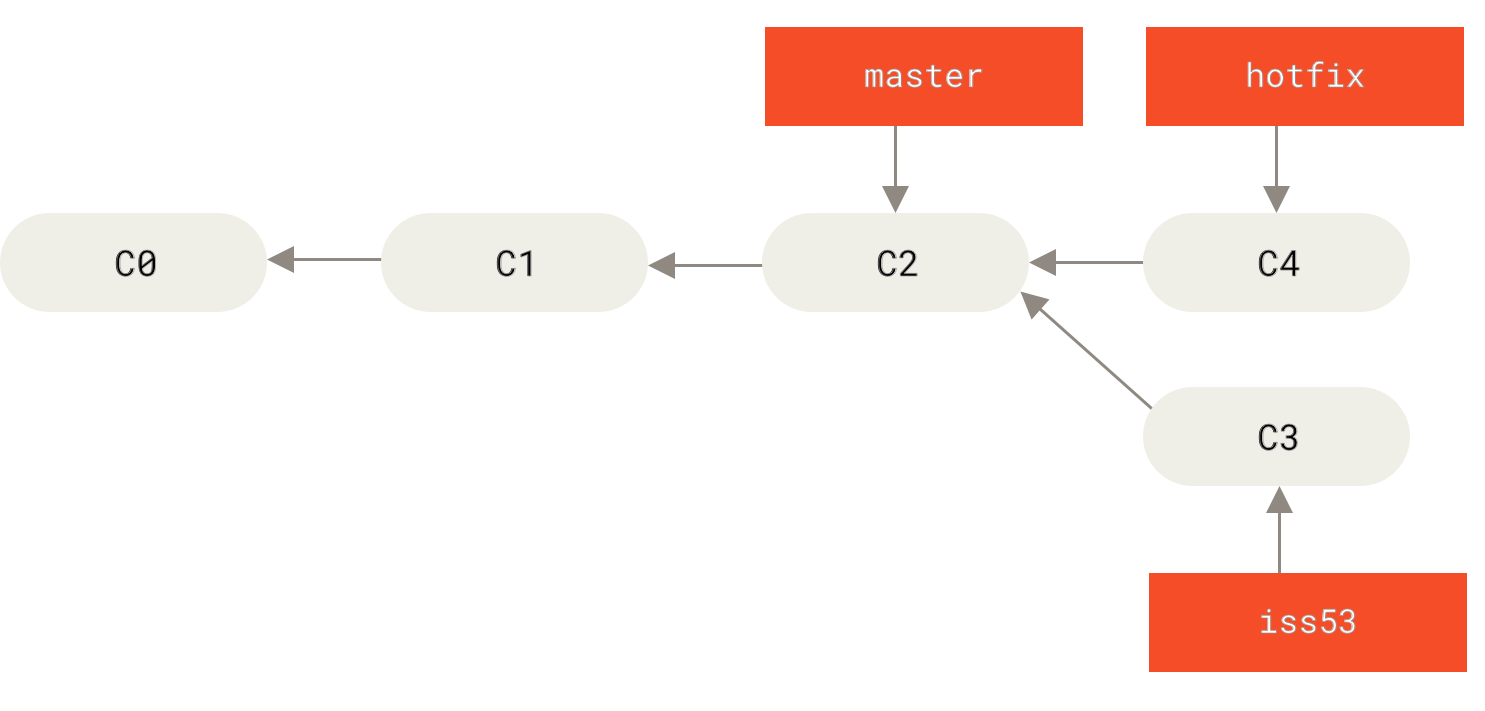
To merge commits from branch iss53, please issue the following commands.
git checkout master
git merge iss53
After that, you would push the master branch to Github for deployment.
git push -u origin master
More Github features
Access Github with SSH keys
Please click on New SSH key, you could give it a name and input the key.
ssh-keygen
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Collaboration
After repository created, project leader/manager would enable access for project team members to access the repository.
To do so on Github repository, please click on Settings tab on the top bar.
Then, please click Collaborators on left menu. Input Github username of your team member and click Add Collaborator.
After adding team members to the repository, let’s click on Project tab in your repository top bar.